Procedures to Create a Timeline with MindOnMap: German History Timeline
Germany history is like a complicated but interesting patchwork quilt, made up of old times, medieval lords and ladies, and modern-day problems. Making a timeline can be super helpful to get why these events matter and see how they're all linked together. Making a timeline helps you in many ways, such as sorting out what's important, spotting trends and repeating themes, pinpointing how one thing leads to another, and falling in love with German history more. In this guide, we will show you how to make a timeline of German history using MindOnMap. It's a cool tool that lets you put information, see how everything is connected, and create fun timelines.
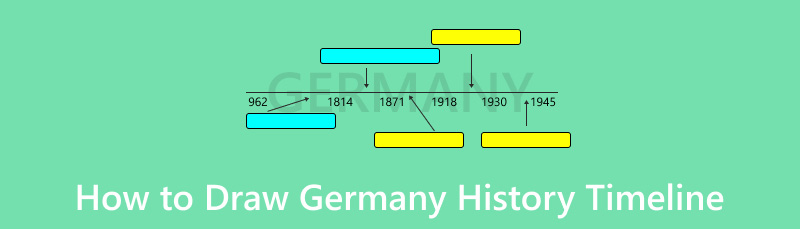
- Part 1. How to Draw Germany History Timeline
- Part 2. Germany History Explanation
- Part 3. FAQs on How to Draw Germany History
Part 1. How to Draw Germany History Timeline
Have you ever been curious about the history of Germany? Making a timeline can be a great way to dive into this deep history story in a fun way. In this guide, we'll teach you to make a timeline about Germany using MindOnMap, an easy-to-use mind-mapping tool that makes it easy to sort out information and see how things are connected.
MindOnMap is a handy tool for making cool and detailed timelines. It has great features that help you sort out info, see how things are connected, and interestingly tell the story of German history. You can arrange events and people from oldest to newest to show how German history unfolded. It has shapes, lines, and pictures to show different historical times, important people, and big events. You can include detailed descriptions, dates, and other important details for each event. Changing the colors and fonts can also make your timeline look how you want. The following are the steps on how to draw a Germany history timeline with this great timeline maker.
Secure Download
Secure Download
Open the internet browser and click this link: https://www.mindonmap.com/
Begin by picking a central topic, like the German History Timeline. Create smaller topics for the big events and times in German history. Click the Main Topic, and the Subtopic highlights the period.
Use lines or arrows to link the smaller topics, showing the order of events. Add pictures or other details to give more background and details. Changing the colors and fonts can help determine the events of the timeline.
Finish your Germany timeline. Once you've done this, save the project and click Share. Here is the link to the Germany timeline.
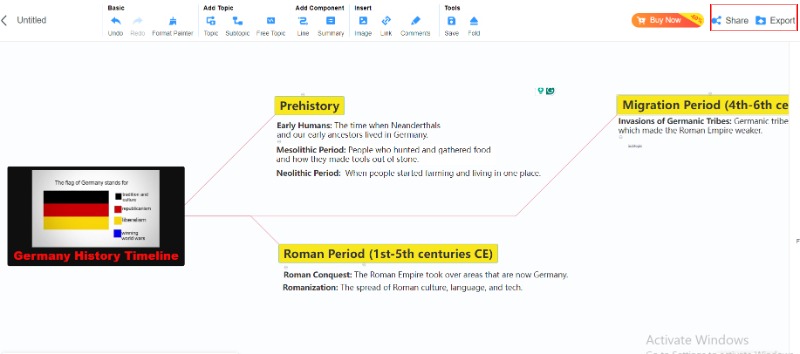
Part 2. Germany History Explanation
Curious about Germany's awesome history? There's so much to discover from its olden days to today's cool tech. In this guide, we will explore history, looking at the big moments, important people, and cultural impacts that made Germany what it is today. To make a history timeline, you must learn the history thoroughly. Here is a brief history about Germany:
Prehistory
• Early Humans: Germany was home to both Neanderthals and early modern humans. They hunted, gathered, and used stone tools. Neanderthal remains suggest they lived there over 40,000 years ago.
• Mesolithic Period: After the Ice Age, people in Germany were hunter-gatherers, using advanced stone tools for hunting and food.
• Neolithic Period: Around 5500 BCE, people began farming. It led to permanent settlements and a new society.
Roman Period (1st-5th centuries CE)
• Roman Conquest: The Roman Empire grew by taking over areas in modern-day Germany, setting up military bases and cities like Cologne and Trier.
• Romanization: Roman ways of life, technology, and how they ruled affected the Germanic tribes. They built roads, forts, and trade routes that still impact the area today. However, the Rhine River kept the area on the edge, with the Romans only having control of the west.
Migration Period (4th-6th centuries CE)
• Invasions of Germanic Tribes: The fall of the Roman Empire led to more Germanic tribes, like the Goths, Vandals, and Franks, moving into the area. It helped cause the collapse of the Western Roman Empire.
• Formation of Germanic Kingdoms: As Rome's power decreased, Germanic tribes formed their kingdoms. The Franks, led by the Merovingians and Carolingians, grew strong and set the stage for later Germanic nations.
Middle Ages (5th-15th centuries)
• Carolingian Empire (751-887): Charlemagne led the Carolingian Empire to power in Europe, becoming Emperor of the Romans in 800 and restoring imperial control in Western Europe.
• Holy Roman Empire (962-1806): Otto I became emperor in 962, creating the Holy Roman Empire, a loose alliance of states that grew to include much of Germany, Austria, Italy, and France.
• Crusades: German nobles and knights joined the Crusades. They were Church-approved wars to reclaim the Holy Land from Muslims.
• Black Death: The Black Death, a deadly pandemic in the 14th century, devastated Germany and other parts of Europe and led to significant social and economic changes.
Early Modern Period (15th-18th centuries)
• Reformation (1517): Martin Luther, a German monk, began the Protestant Reformation in 1517 by criticizing the Catholic Church with his 95 Theses, leading to major religious and political changes in Europe and splitting Germany into Protestant and Catholic areas
• Thirty Years' War (1618-1648): The Thirty Years' War (1618-1648) was a devastating conflict between Protestant and Catholic states, leaving Germany in ruins. The Peace of Westphalia ended the war but also left the country divided and weakened.
• Rise of Prussia: In the 18th century, Prussia rose to power under Frederick the Great, growing its territory and influence, eventually leading to Germany's unification.
19th Century
• Unification of Germany (1871): Otto von Bismarck, the Prussian chancellor, led Germany to unification in 1871 after defeating Austria and France in wars. It resulted in the creation of the German Empire, with King Wilhelm I of Prussia becoming Emperor.
• Industrial Revolution: In the late 1800s, Germany became a top industrial and military power, making major technological and scientific advancements.
• World War I (1914-1918): Germany was a key player in World War I (1914-1918), which ended in defeat. It led to the abdication of Kaiser Wilhelm II and the rise of the Weimar Republic. Germany signed the Treaty of Versailles, which imposed heavy reparations, which caused ongoing political issues.
20th Century
• Weimar Republic (1918-1933): After World War I, Germany became a democratic republic but faced challenges like hyperinflation, political extremism, and economic depression, which caused its downfall.
• Nazi Germany (1933-1945): In 1933, Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party seized power, creating a dictatorship. They aggressively expanded, leading to World War II and the Holocaust, the genocide of six million Jews and others.
• Post-War Germany: Germany split into East and West after losing the war. West Germany became a democratic state with ties to the West, while East Germany was a communist state under Soviet control.
• Modern Germany: Germany is a major EU influence famous for its strong economy, tech progress, and stable politics. It leads to tackling worldwide issues like climate change, immigration, and diplomacy.
Part 3. FAQs on How to Draw Germany History
When did Germany's history start?
Germany's history dates back to 1 CE with Germanic tribes and the Holy Roman Empire (962 CE) under Otto I. It became modern Germany 1871 under Otto von Bismarck, forming the German Empire. Its history includes early human settlements and interactions with the Roman Empire from the 1st to 5th centuries CE.
What big events happened in Germany?
Germany's history includes the Roman Conquest (1st-5th centuries CE): The Roman Empire ruled some parts of Germany. Holy Roman Empire (962 CE): A major European political group for over a thousand years. Protestant Reformation (1517): Martin Luther's movement split the Catholic Church. It changed religion and politics. Thirty Years' War (1618-1648): A war that devastated Germany. German Unification (1871): Otto von Bismarck united German states into one country. World War I (1914-1918): Germany lost, causing political and economic problems. Nazi-Era and World War II (1933-1945): Adolf Hitler became the leader in WWII and the Holocaust. Division and Reunification (1949-1990): Germany was split into East and West after WWII and reunited in 1990.
What was Germany called in Roman times?
In Roman times, Germany called Germania. The Romans used this term to describe the region east of the Rhine River, inhabited by various Germanic tribes. The Roman Empire never fully conquered Germany, though it had temporary control over parts of western Germany.
Conclusion
In summary, exploring the history of Germany is an intriguing experience that shows its deep and complicated history. MindOnMap is a useful tool for visually showing this timeline, helping to understand important events and changes in Germany's history. It's a great way to highlight Germany's role and development.











