European History Timelines Help Tease Out History
The history of Europe is an epic of diversity and integration. It has witnessed the glory of classical civilization, the rise and fall of the feudal system in the Middle Ages, the global transformation led by the modern Industrial Revolution…
The history of Europe is a symphony of war and peace, a palace of art and science, and an immortal chapter of humankind's exploration of the unknown and pursuit of progress. This article will use the European history timelines to help you understand European history.
- Part 1. General European History Timeline
- Part 2. 19th-century European History Timeline
- Part 3. 20th-century European History Timeline
- Part 5. FAQs
Part 1. General European History Timeline
Here is a self-made European history timeline. Follow us to have a better understanding of European history.

Ancient Civilizations (3000 BCE - 4th Century CE)

• Aegean Period: Laid the foundation for European culture. This period included the Minoan civilization (around 2800-1500 BCE) and the Mycenaean civilization (around 1600-1200 BCE), both representing the Bronze Age.
• Ancient Greece: Beginning in the 8th century BCE, ancient Greece emerged as the cradle of Western civilization.
Roman Period (500 BCE - 476 CE)
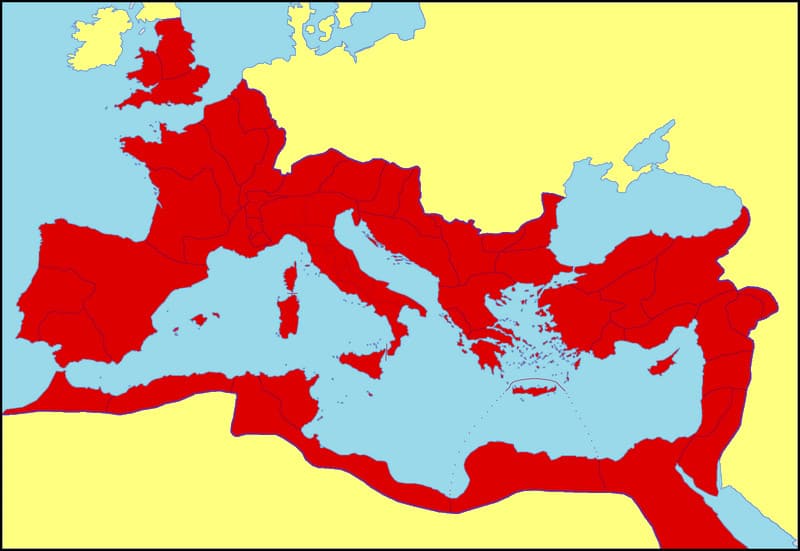
• Roman Republic: Established in 509 BCE, the Roman Republic expanded and fought numerous wars, eventually becoming the dominant power in the Mediterranean region.
• Roman Empire: In 27 BCE, Augustus became the first emperor of the Roman Empire.
• Fall of the Western Roman Empire: In 476 CE, the Western Roman Empire fell to Germanic tribes, signaling the start of the Middle Ages in Europe.
Middle Ages (5th Century - 15th Century)

• Formation of Feudalism: In the early Middle Ages, feudalism gradually emerged in Europe, establishing a complex hierarchy among kings, nobles, and knights.
• Rise of Religion: Christianity became the dominant force in medieval European society, with the Church playing significant roles in politics, economics, and culture.
• Crusades: Launched to reclaim the Holy Land from Muslim control, the Crusades had profound impacts on European history.
Renaissance (14th - 16th Century)

• Renaissance Emergence: The Renaissance was an intellectual and cultural movement that occurred from the 14th to the 16th century. Originating in Italy, it quickly spread throughout Europe. Renaissance thinkers rediscovered classical culture and art, advocating humanism, individual expression, and free thought.
• Art and Science Development: Renaissance artists produced numerous paintings, sculptures, and architectural works, such as Leonardo da Vinci's Mona Lisa and Michelangelo's David. Science also made great strides, with Copernicus proposing the heliocentric model of the universe.
Modern Era (16th - 19th Century)

• Reformation: Martin Luther's Reformation movement in the 16th century critically examined and reformed the Catholic Church, leading to the emergence of Protestantism and the fragmentation of the Catholic Church.
• Scientific Revolution: During the 17th and 18th centuries, Scientific Revolution happened in Europe, with scientists proposing new theories and methods, such as Newton's law of universal gravitation, laying the foundation for modern science.
• Industrial Revolution: From the late 18th to mid-19th century, the Industrial Revolution transformed Europe's economy and society by replacing manual labor with machine production, significantly boosting productivity.
Contemporary Era (19th Century - Present)

• Rise of Nation-States: In the 19th century, modern nation-states emerged in Europe, fueled by nationalist sentiment.
• World Wars: Europe endured two devastating world wars in the 20th century, which brought profound suffering and destruction but also prompted political, economic, and social transformations.
• Cold War and Globalization: After World War II, Europe entered the Cold War era with the United States and the Soviet Union competing for influence. With the end of the Cold War and the acceleration of globalization, Europe has integrated into the global landscape, becoming a significant force in world economics and politics.
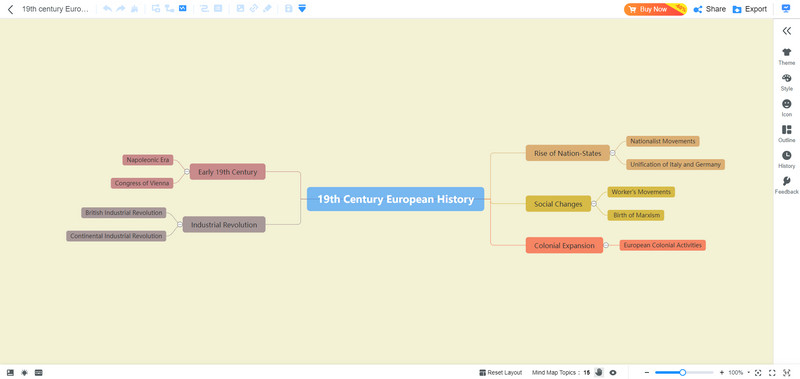
Part 2. 19th-century European History Timeline
The 19th and 20th centuries were two extremely important periods in European history, and these two centuries witnessed great changes in Europe and even the world.
Here is a 19th-century European history timeline.

Early 19th Century
• Napoleonic Era: Napoleon Bonaparte established the First French Empire in 1804, embarking on a series of wars across the European continent that reshaped its political map.
• Congress of Vienna: In 1815, to rearrange the European order after the Napoleonic Wars, European powers convened in Vienna, establishing the principle of the "Concert of Europe."
Industrial Revolution

• British Industrial Revolution: In the first half of the 19th century, Britain led the way in the Industrial Revolution, where machine production gradually replaced hand labor, significantly boosting productivity.
• Continental Industrial Revolution: Subsequently, the Industrial Revolution spread to continental Europe, with Germany and France entering the industrial age.
Rise of Nation-States
• Nationalist Movements: With the advancement of the Industrial Revolution and the awakening of national consciousness, nationalist movements emerged across Europe, fostering the formation of nation-states.
• Unification of Italy and Germany: In the mid-19th century, Italy and Germany achieved unification through a series of wars and diplomatic maneuvers.
Social Changes

• Worker's Movements: As industrialization deepened, the working class grew and began to organize for their rights, exemplified by the Lyon Uprisings in France and the Chartist Movement in Britain.
• Birth of Marxism: The publication of the Communist Manifesto in 1848 marked the birth of Marxism, providing a theoretical foundation for subsequent socialist movements.
Colonial Expansion
• European Colonial Activities: The 19th century saw a peak in European colonial expansion, with European powers controlling vast areas of the world through military or economic means.
Part 3. 20th-century European History Timeline
Next, let's learn about the events in the 20th century in Europe with a 20th-century European history timeline.
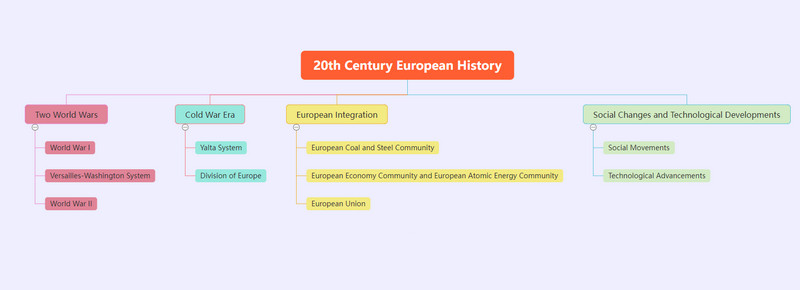
Two World Wars

• World War I: From 1914 to 1918, major European countries were embroiled in a devastating war, resulting in tens of millions of casualties and immense economic losses.
• Versailles-Washington System: After the war, a new international order was established through treaties like the Treaty of Versailles, but this system remains unstable, foreshadowing future conflicts.
• World War II: From 1939 to 1945, Europe plunged into war again as Axis powers like Nazi Germany and Fascist Italy clashed with the Allies.
Cold War Era
• Yalta System: After WW II, the United States and the Soviet Union emerged as superpowers, dominating the global landscape. They divided spheres of influence through mechanisms like the Yalta Conference, leading to the Cold War rivalry.
• Division of Europe: Germany was split into East and West, and Europe was divided into socialist and capitalist blocs.
European Integration

• European Coal and Steel Community (ECSC): In 1951, six European countries founded the ECSC, marking the beginning of European integration.
• European Economic Community (EEC) and European Atomic Energy Community (Euratom): Subsequently, these countries established the EEC and Euratom.
• European Union (EU): In 1993, the EEC was renamed the EU, further advancing political and economic integration in Europe.
Social Changes and Technological Developments
• Social Movements: Europe witnessed various social movements in the 20th century, such as feminism and environmentalism, driving social progress and transformation.
• Technological Advancements: In the realm of technology, Europe has achieved numerous significant accomplishments, including advancements in quantum mechanics and the rise of computer technology.
Part 4. Bonus: Best Timeline Creator
You have seen the above 3 timelines, and they are very powerful to help you comb the big events, right? Let's show you the best timeline creator: MindOnMap.
MindOnMap is a mind-mapping tool for creating European history timelines. It can be used online or downloaded for Mac and Windows computers. MindOnMap specializes in creating mind maps that help you organize your thoughts, plan your work, and study. Besides, it provides multiple templates and themes that enable you to make your personalized style. Moreover, you can share the links of the finished timelines with your friends or export the SD, JPG, or PNG images for free.
Part 5. FAQs
What are 5 key dates in European history?
1. In 753 BC, the city of Rome was founded, marking the beginning of Roman civilization.
2. In 476 AD, the Western Roman Empire fell, marking the end of the Roman era and the beginning of the Middle Ages.
3. In 1453 AD, the fall of Constantinople was a symbol of the decline of the Byzantine Empire and a major shift in the balance of power between East and West.
4. In 1517, Martin Luther launched the Reformation, a major ideological liberation movement in European history.
5. In 1789, the French Revolution broke out, a major political revolution in European history, which overthrew the feudal autocracy and established a bourgeois democratic republic.
When did Europe first appear?
During the ninth-century Carolingian Renaissance, the term "Europe" was originally applied to a cultural sphere.
What is the oldest civilization in Europe?
The Minoan civilization was the oldest in Europe.
Conclusion
Today, we use 3 timelines of European history to help sort out its history and introduce the best timeline maker, MindOnMap. The mysteries of history are fascinating. They are often hidden in a sea of historical documents, archaeological finds, legends, etc. If you are interested in the history, MindOnMap would be your best helper! Brave to have a try!










